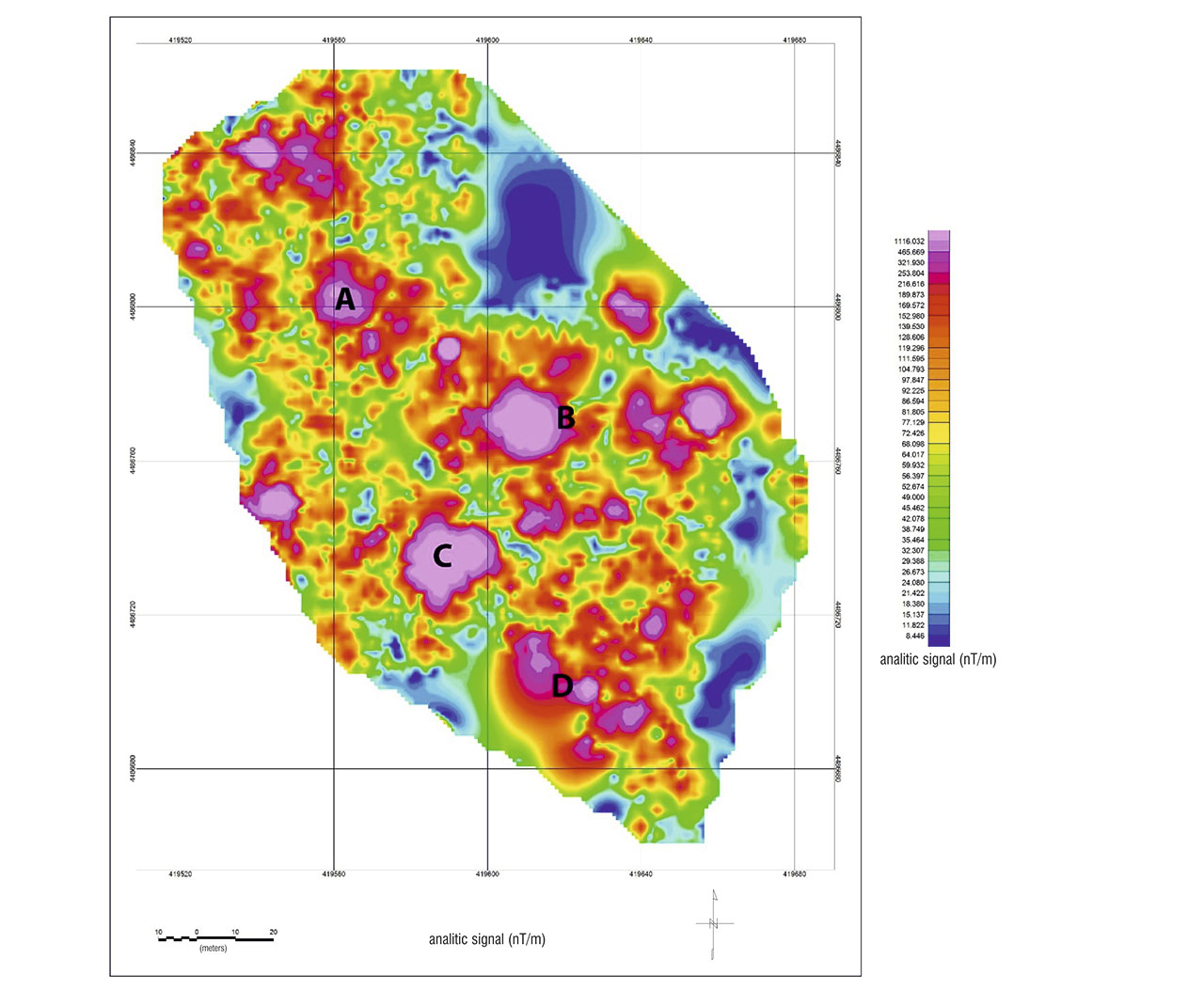
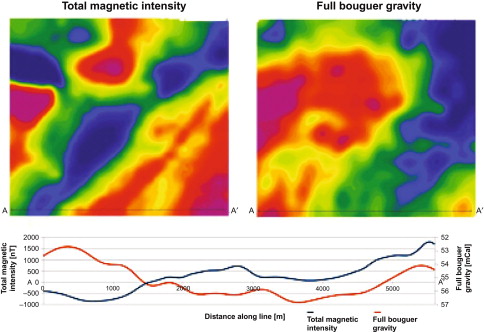
Magnetics
The magnetometer, an instrument utilized in geophysical studies, quantifies the scalar measurement of the Earth's complete magnetic field strength in nanotesla (nT). In environmental contexts, the presence of ferromagnetic materials within the near-surface subsurface generates discernible irregularities in the overall magnetic field. As a consequence, noteworthy anomalies can arise, signifying the existence of buried metallic objects, a phenomenon readily detectable through magnetometer surveys. These anomalies can arise from either induced magnetism or residual magnetism. Induced magnetism involves an augmentation of the prevailing magnetic field owing to a material's responsiveness to the field, causing it to exhibit magnetic properties. The resultant magnetization is directly linked to the intensity of the prevailing magnetic field and the material's capacity to amplify the local magnetic field's strength, known as magnetic susceptibility. Magnetometer surveys, therefore, offer a valuable means of mapping subsurface metallic features, unraveling the complex interplay of magnetic forces within the Earth's shallow layers and providing insights into both geological and archaeological realms.